Hair loss is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide, yet it remains a source of concern and confusion.
Understanding the causes, types, and treatment options is essential for anyone experiencing hair shedding, thinning, or receding. Whether it’s genetic, hormonal, or lifestyle-related, hair shedding can impact confidence and quality of life.
This comprehensive guide explains everything you need to know about hair loss, including natural regrowth strategies, medical treatments, and the best products to support healthy hair.
By the end, you’ll also know when to consult a hair loss specialist near you to create a personalized plan.
What Is Hair Loss?
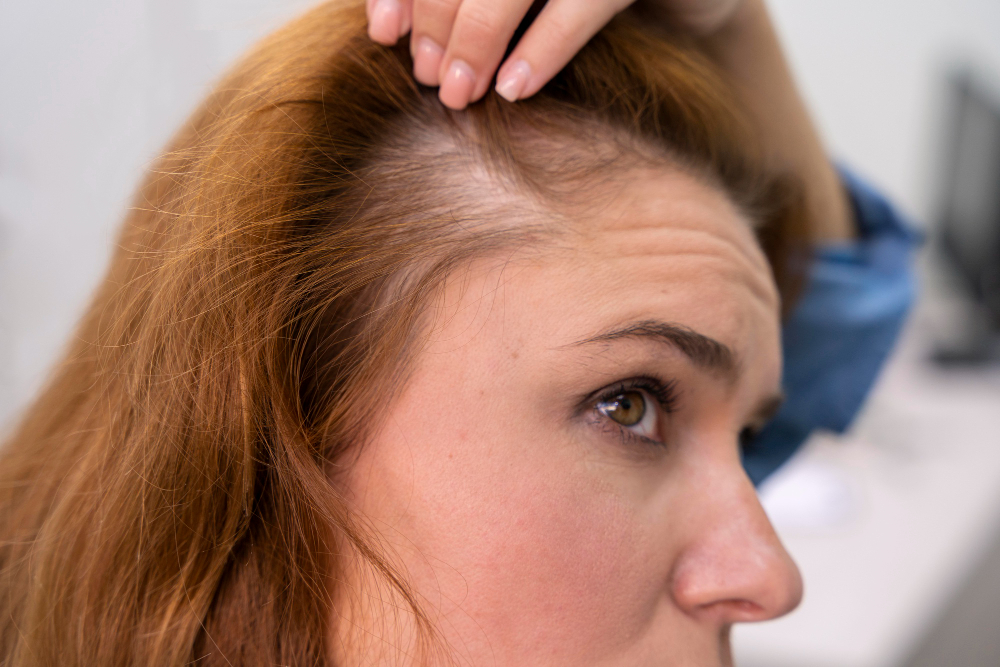
Hair loss, medically known as Alopecia, refers to the thinning or shedding of hair from the scalp or other parts of the body. While shedding 50–100 hairs per day is normal, persistent or excessive hair loss may indicate an underlying condition.
Types of Hair Loss
- Androgenetic Alopecia – Commonly known as male or female pattern baldness, caused by genetics and hormones.
- Telogen Effluvium – Temporary hair shedding triggered by stress, illness, or sudden lifestyle changes.
- Alopecia Areata – An autoimmune condition causing patchy hair loss.
- Traction Alopecia – Hair loss due to hairstyles that pull on the hair over time.
Quick Facts:
- Men often experience hair loss starting in their 20s to 30s.
- Women typically notice thinning after menopause.
- Both genetics and environment play a role in hair health.
💡 Extra Tip: Track your hair thinning by gently collecting shed hairs after brushing or washing. Patterns over time can indicate whether you are experiencing normal shedding or a more serious condition.
👉 Learn more here: Hair Loss vs Hair Shedding
Causes of Hair Loss

Hair loss can result from a variety of factors that often act in concert. Some of the most common causes include:
- Genetic Predisposition: Female pattern hair loss (FPHL) and male pattern baldness are hereditary conditions. If your family has a history of hair thinning or baldness, you may be more prone to it. 👉 Learn more: What Causes Female Pattern Hair Loss.
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy, menopause, thyroid disorders, and other hormonal fluctuations can disrupt the hair growth cycle, leading to temporary or permanent hair loss.
- Stress and Lifestyle: Chronic stress, lack of sleep, and high-sugar diets can contribute to reduced hair density. Studies show that sugar spikes may trigger hormonal changes that weaken hair follicles. 👉 Explore more: Hair Loss and Sugar: What’s the Link | Stress and Scalp Health
- Medical Conditions & Medications: Certain illnesses (e.g., autoimmune diseases, diabetes) or medications (e.g., chemotherapy, blood thinners) can trigger Alopecia.
- Hair Treatments & Styling Practices: Overuse of chemical relaxers, frequent bleaching, tight hairstyles, and heat styling can damage hair shafts and follicles over time. 👉 More info: Chemical Hair Relaxer
🔬 Research Insight: A review on telogen effluvium (TE) — a common diffuse condition — found that stress, illness, and hormonal imbalances can trigger premature follicle shifts into the telogen phase, leading to noticeable shedding.
💡 Extra Tip: Identifying the root cause can dramatically improve outcomes. A professional scalp analysis can help detect issues before significant thinning occurs.
Understanding the Hair Growth Cycle
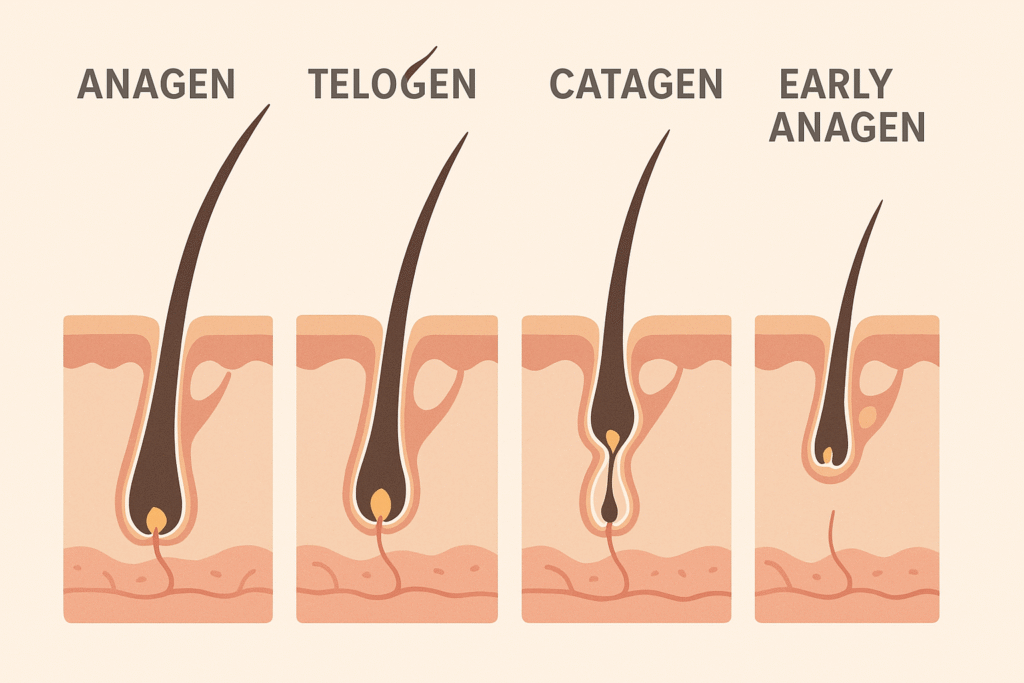
Hair grows in a continuous cycle composed of three main phases:
- Anagen (Growth Phase): Lasts 2–6 years. Hair actively grows from the follicle. Genetics largely determines hair length.
- Catagen (Transition Phase): A brief 2–3 week period where hair growth slows, and the follicle shrinks.
- Telogen (Resting Phase): This phase lasts approximately 3 months. Hair sheds naturally at the end of this phase.
Disruption in any phase—due to stress, poor nutrition, or scalp issues—can accelerate or prolong shedding. Understanding this cycle helps in choosing effective treatments.
👉 For more details: Hair Growth Cycle Explained and Protein Overload in Hair
💡 Extra Tip: Keeping a hair journal, noting shedding patterns, diet, and hair care habits, can reveal triggers affecting your hair cycle.
How to Regrow Hair Naturally

If you prefer non-medical approaches, several natural strategies can support hair regrowth and strengthen existing hair.
1. Scalp Massage & Stimulation
Massaging the scalp improves blood flow, promoting nutrient delivery to hair follicles.
2. Natural Oils
- Rosemary oil – Stimulates follicle activity.
- Castor oil – Thickens hair over time.
- Peppermint oil – Encourages hair growth.
3. Nutrition & Supplements
Ensure your diet includes:
- Protein-rich foods
- Iron and zinc sources
- Biotin or other hair-supporting vitamins
4. Lifestyle Adjustments
- Reduce stress through meditation, yoga, or regular exercise.
- Get 7–8 hours of sleep nightly.
5. Low-Level Laser Therapy
Clinically proven devices can stimulate hair follicles and improve hair density over time.
Treatments for Hair Loss
Medical treatments offer practical solutions for different types of hair thinning.
1. Over-the-Counter Treatments
- Minoxidil – Applied topically to stimulate hair growth.
- Hair growth shampoos – Containing biotin or caffeine.
👉 Compare options here: Professional vs DIY Hair Treatments.
2. Prescription Treatments
- Finasteride – Oral medication for men that blocks DHT.
- PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) therapy – Uses your blood’s growth factors to encourage regrowth.
3. In-Clinic Procedures
- Hair Transplants – Moving healthy follicles to thinning areas.
- Scalp Injections – Medications delivered directly to follicles.
| Treatment | Effectiveness | Timeline |
|---|
| Minoxidil | Moderate | 3–6 months |
| Finasteride | High (men only) | 3–6 months |
| PRP Therapy | High | 3–6 sessions |
| Hair Transplant | Very High | Permanent |
💡 Extra Tip: Pair scalp treatments with gentle hair care routines, avoiding harsh chemical treatments and excessive heat to maximize results.
👉 Learn more: Expert Hair Care Tips
Best Products for Hair Loss & Hair Breakage

Supporting hair health with quality products can improve regrowth outcomes.
- Sulfate-Free Shampoo – Gentle cleansing, reduces breakage
- Strengthening Conditioner – Rebuilds hair structure
- Bond-Repair Masks – Restores damaged hair
- Hair Growth Serums – Boosts follicle activity
Daily Hair Care for Prevention
- Use gentle, sulfate-free shampoos.
- Avoid excessive heat styling.
- Maintain scalp hygiene to prevent buildup.
- Follow expert hair care tips.
- Maintain hair health at home: Hair Care Maintenance
💡 Extra Tip: Reduce sugar intake and stay hydrated for optimal follicle health.
Hair Extensions & Hair Loss

Improper care of extensions can cause strain on the hair and exacerbate shedding.
👉 Read: Tip for Hair Loss and Extensions
Table: Recommended Post-Extension Hair Care by Hair Type and Extension Type
| Hair Type | Extension Type | Recommended Care | Frequency | Products/Tools |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fine | Tape-In | Gentle sulfate-free shampoo, lightweight conditioner | 2-3x/week | Soft-bristle brush |
| Medium | Keratin Bond | Deep conditioning, avoid excessive heat | 1x/week | Wide-tooth comb |
| Thick | Clip-In | Clarifying shampoo post-wear, detangle before washing | 1x/week | Detangling spray |
| All Types | Sew-In | Scalp massage, moisturizing scalp treatment | 2x/week | Scalp serum |
Take Control of Your Hair Health Today
Hair loss doesn’t have to be permanent. Understanding the causes and following professional scalp treatments can help strengthen your hair and maintain a healthy scalp. Book a personalized scalp consultation today and start your journey to healthier hair.
FAQ
What does hair loss mean?
Hair loss is the shedding or thinning of hair beyond normal daily amounts. Persistent hair loss may indicate genetic, hormonal, or health-related causes.
What causes sudden hair loss?
Sudden hair loss can result from stress, illness, hormonal changes, medications, or nutritional deficiencies.
How can I regrow hair naturally?
Scalp massages, natural oils, balanced nutrition, and lifestyle improvements can support regrowth. Low-level laser therapy may also help.
What are the best treatments for hair shedding?
Minoxidil, finasteride (for men), PRP therapy, and hair transplant procedures are effective depending on the type and severity of hair loss.
When should I see a doctor for hair loss?
If hair shedding is sudden, patchy, or worsening, consult a hair loss specialist to identify the underlying cause and treatment options.









